Each protein is a collection of several amino acids and these amino acids are called building block of proteins. Depending upon these buildigg blocks, nature of the protein'varies. Building blocks, types and sources of different proteins are described below:
Building Blocks of Protein - Amino acids
There are 22 amino acids that usually makeuplform proteins. Amino acids are covalently linked in proteins in a linear fashion by a linkage called peptide bond.
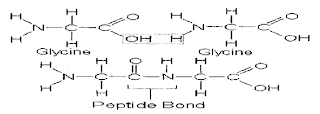 |
| A molecule of water is removed from two glycine amino acids to form a peptide bond |
It is remarkable that though different proteins contain the same set of amino acids, they differ in their arrangement in linear chain to give rise to proteins with diverse functions such as enzymes, antibodies, hormones etc. As the name indicates, amino acids contain at least an amino and a carboxyl group. Based on their chemical properties, amino acids can be grouped into five classes: nonpolar, polar, aromatic, basic and acidic. However, on nutritional basis they are classified as essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids. There are eight amino acids that are grouped under essential amino acids. These are required in the diet because body cannot synthesize them. The remaining amino acids can be synthesized in the body and are therefore non-essential in the diet. However, this classification is ambiguous as all the 22 amino acids are necessary for building body's tissue proteins.
 |
| Classification of amino acids |
Types of Proteins and their Sources
According to the nutritional requirements, proteins are classified as complete or incomplete. This classification is based on the amount of essential amino acids present in a protein. Complete proteins are those that contain all the essential amino acids in sufficient amount and ratio to meet the body's requirements. Proteins of animal origin such as those in egg, meat and milk are considered as complete proteins, whereas proteins derived from plant products such as grains and legumes are incomplete proteins. Poultry, fish, meat, peanuts, wheat germ, cheese are most concentrated protein foods on weight basis. Milk has 3.0 - 3.5 per cent protein whereas cereals such as rice and oat meal and potatoes have only about 2.0 per cent protein. Vegetables and hits have low protein concentrations.
The nutritive value of plant proteins can be improved by complementation. By combining a plant source low in one amino acid with another supplying that amino acid, we can complement or mutually supplement proteins. Vegetarians should use a combination of complementary protein in their diet. For example, beans, peas are rich in lysine but low in sulphur containing amino acids such as methionine and cysteine which can be complemented by including cereals (wheat) in the diet.
Proteins are essential macromolecules that perform a wide range of functions in the body. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, of which there are 20 different types.
ReplyDeleteRead more : what are the building blocks of proteins